- [1] Department of Computer Science and Software Engineering,
The University of Melbourne, Australia 3010.
- [2] School of Computer Science and Software Engineering, Monash University, Australia 3800.
- [3] Department of Microbiology, Monash University, Australia 3800.
- [2] School of Computer Science and Software Engineering, Monash University, Australia 3800.
This document is online at: users.monash.edu.au/~lloyd/Seminars/2001-Malaria/index.shtml and contains hyper-links to more resources.
- Malaria kills 1.5 million to 2.7 million people each year [-W.H.O. 1997]
- Plasmodium falciparum the most deadly organism.
- Its DNA is 80% A-T.
- This bias causes many "false positive" matches if it is not well modelled . . .
<< [02] >>
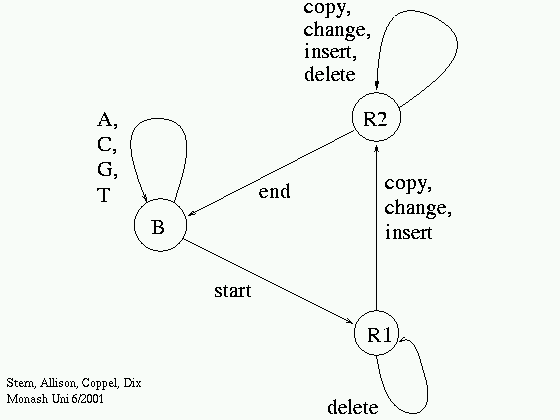
We use
- Probabilistic model (see later or [more here])
- Probabilistic finite-state machine (~ HMM).
- Fit probability parameters to data sequence.
- Sum probabilities of all paths (explanations).
- Criterion: Minimum Message Length [MML]
~ Bayes + compression ~ Shannon entropy
- natural null-theory and significance test
- resists over-fitting
- invariant, consistent
<< [03] >>
<< [04] >>
<< [05] >>
<< [06] >>
<< [07] >>
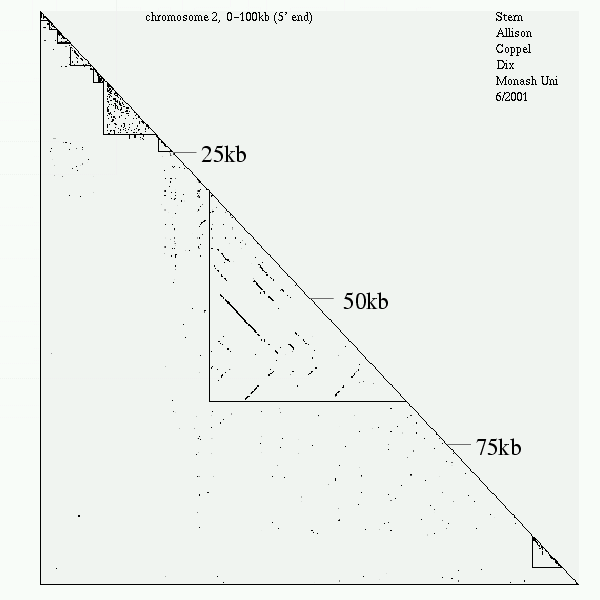
<< [08] >>
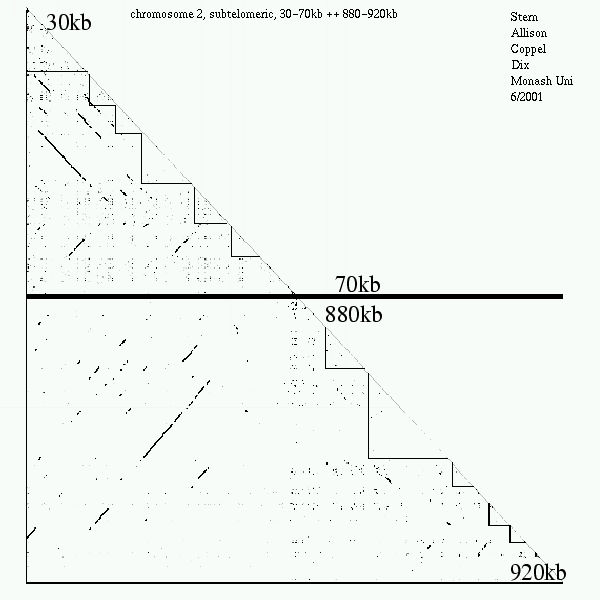
<< [09] >>
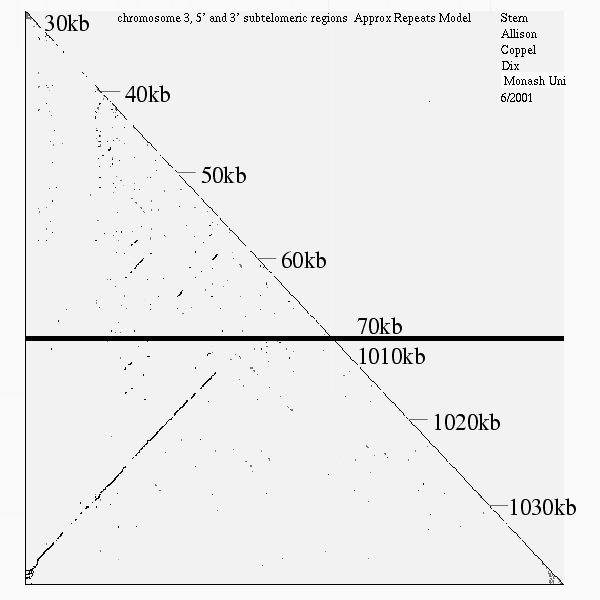
<< [10] >>
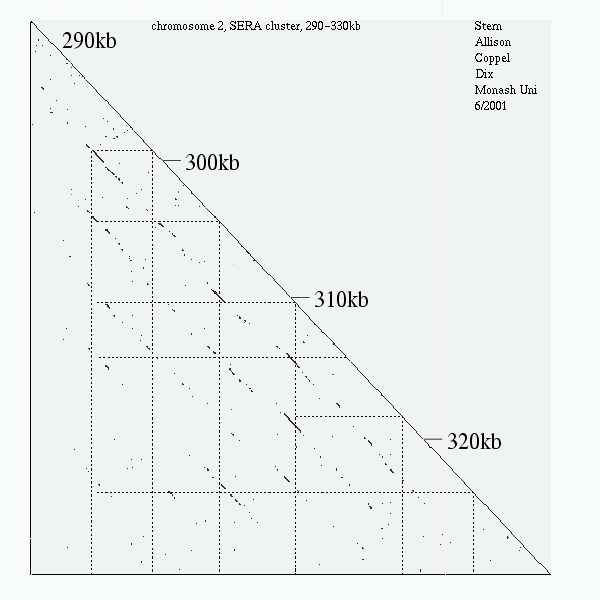
<< [11] >>
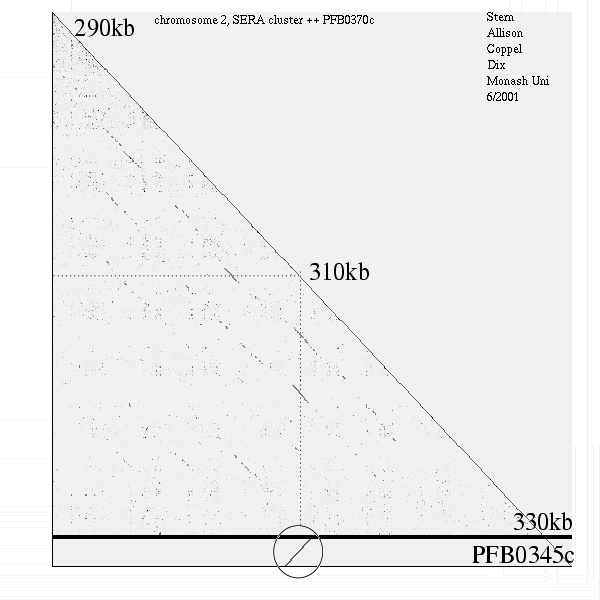
<< [12] >>
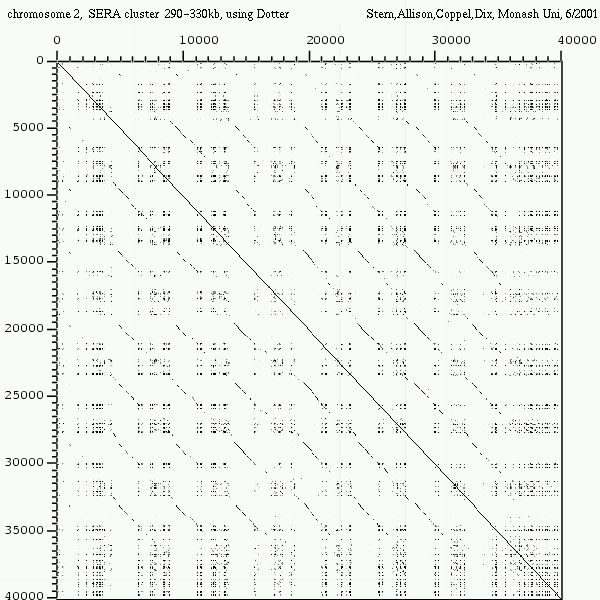
<< [13] >>
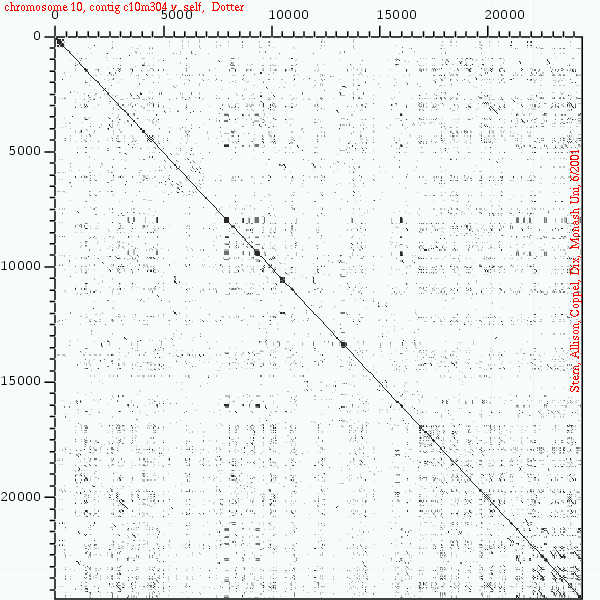
<< [14] >>
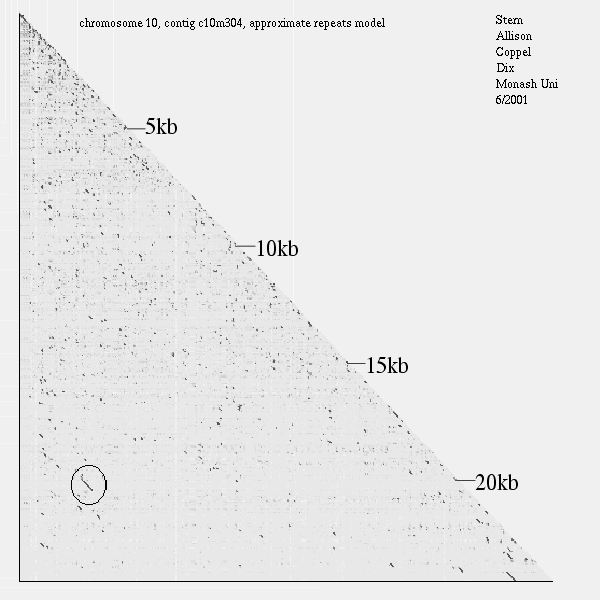
<< [15]
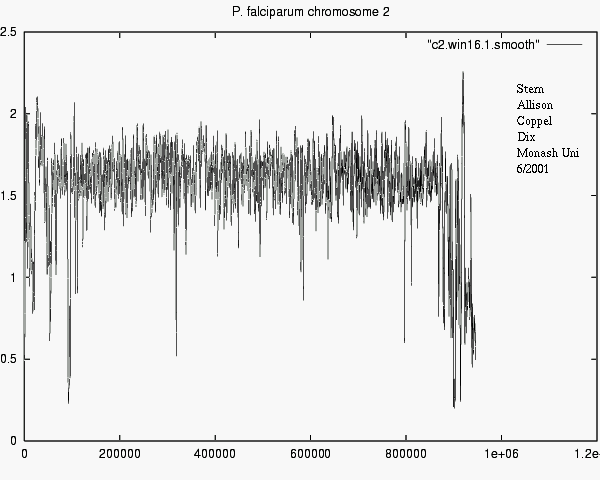
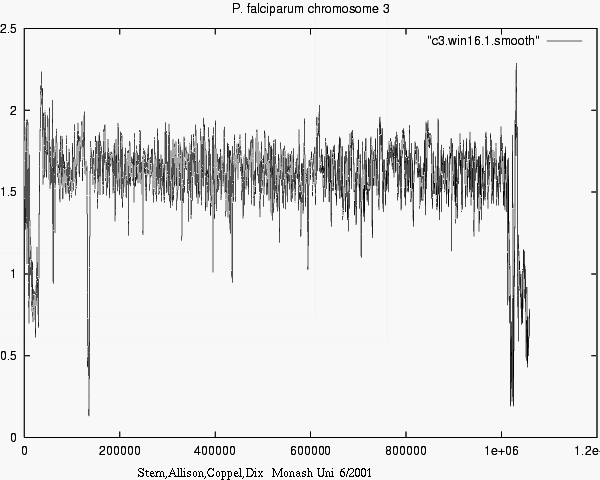
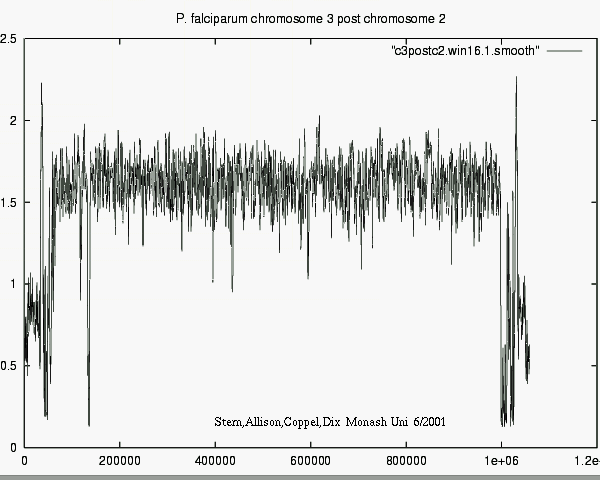
CONCLUSIONS
- Modelling can account for "mere" background properties,
- i.e. ignoring non-news,
- revealing significant matches, i.e. real news.
- Differences in information show e.g. what
new or surprising information Chr_i tells about Chr_j.
- 1-D plots are 1-D !
i.e. Feasible for l o n g sequences.
- See: L. Stern, L. Allison, R. L. Coppel, & T. I. Dix. Discovering patterns in Plasmodium falciparum genomic DNA. Molecular and Biochemical Parasitology, 118 pp175-186, 2001.