Surface Acoustic Wave Microchannel Actuation

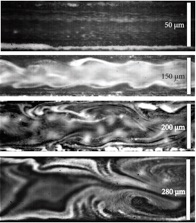
In addition, we have also shown the possibility of transporting and mixing fluid in paper-based microfluidic systems. Unlike passive capillary-based transport through the paper network, the SAW-induced actuation allows for faster flow as well as more uniform and precise mixing.
-
1.MK Tan, LY Yeo, JR Friend. Rapid Fluid Flow and Mixing Induced in Microchannels using Surface Acoustic Waves. Europhys Lett 87, 47003 (2009) (PDF).
-
2.MK Tan, R Tjeung, H Ervin, LY Yeo, J Friend. Double Aperture Focusing Transducer for Controlling Microparticle Motions in Trapezoidal Microchannels with Surface Acoustic Waves. Appl Phys Lett 95, 134101 (2009) (PDF).
-
3.MK Tan, LY Yeo, JR Friend. Unique Flow Transitions and Particle Collection Switching Phenomena in a Microchannel Induced by Surface Acoustic Waves. Appl Phys Lett 97, 234106 (2010) (PDF).
-
4.AR Rezk, A Qi, JR Friend, WH Li, LY Yeo. Uniform Mixing in Paper-Based Microfluidic Systems Using Surface Acoustic Waves. Lab Chip 12, 773–779 (2012) (PDF).
-
5.MB Dentry, J Friend, LY Yeo. Continuous Flow Actuation Between External Reservoirs in Small-Scale Devices Driven by Surface Acoustic Waves. Lab Chip 14, 750–758 (2014) (PDF).
-
6.MB Dentry, LY Yeo, JR Friend. Frequency Effects on the Scale and Behavior of Acoustic Streaming. Phys Rev E 89, 013203 (2014) (PDF).
Up: Surface acoustic wave microfluidics
Previous: Surface acoustic wave driven microcentrifugation and the Lab-on-a-Disc platform
Next: Surface acoustic wave interfacial jetting


