 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
|
Extended
Kalman Filter (EKF) :
|
|
|
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
The EKF is a statistical assimilation technique that updates
the soil moisture profile based on the
|
|
relative magnitudes of the covariances of the observations and the model profile
estimates. The main
|
advantage
of EKF is that the entire profile may be updated because of the correlation between
the
|
|
surface
soil moisture and the soil moisture of deeper soil. The algorithm tracks
the conditional mean
|
|
|
of a
statistically optimal estimate of a state vector X through a series of forecast and update steps.
|
|
|
|
|
 |
 |
Forecast
steps:
|
|
Project the State ahead:
|
|
|
Project the error Covariance ahead:
|
|
|
|
|
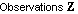 |
|
|
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
Update
steps:
|
|
Compute the Kalman gain:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
 |
Update State
estimate with
observation zn+1:
|
|
Update
the error Covariance:
|
|
|
|
|
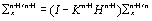 |
|
|























