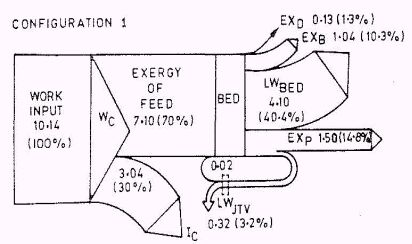
The exergy of a system is the maximum useful work that can be extracted from that system until it reaches equilibrium with its environment. Exergy can be destroyed by irreversibilities of a process. An exergy analysis (or 2nd Law analysis) is a very powerful way of optimizing complex thermodynamic systems. In the context of PSA, an exergy analysis can be used to identify which components of the system are responsible for irreversibility, or lost work and developments can then be directed at those components. The diagram below (from R.Banaerjee, et al."Exergy analysis of pressure swing adsorption processes for air separation", Chemical Engineering Science 45(2), pg467,1990) shows an example of Grassman diagram which is a graphical depiction of the exergy flows during operation of a PSA system.
Work enters through the compressors (100% of the input exergy) and exits the system at various points along the way. Note that the exergy destroyed in the PSA beds amounts to 40% of the input exergy, a significant fraction. It is this component that can be addressed by intelligent cycle design. Typical PSA plants contain adsorbent beds, compressors, valves, and tanks. Common irreversibilities are pressure drop during flow through valves, inefficiencies of the compressors, heat transfer from/to the adsorbent beds, mixing of gases within the adsorbent beds and tanks, and mixing of gas streams with the environment. While exergy calculations for many of these components can easily be done (and has been done in earlier studies), it is the exergy destroyed within the adsorbent beds that is of most interest to us since this feature will help guide cycle design. To calculate exergy associated with adsorption/desorption, it is necessary to develop equations based on Adsorption Thermodynamics.
Our research program is directed at developing detailed models for PSA systems including exergy analysis which, together with overall capital and operating cost methods will allow us to optimize the design and operation of PSA systems. For more information on this project, contact Paul Webley.